Market Context Forward From the Analyst
The importance of broadband connectivity is indisputably greater now than ever. The immediate need to help mitigate the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the ongoing broader objectives of delivering on the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), are accelerating the requirement for broadband.
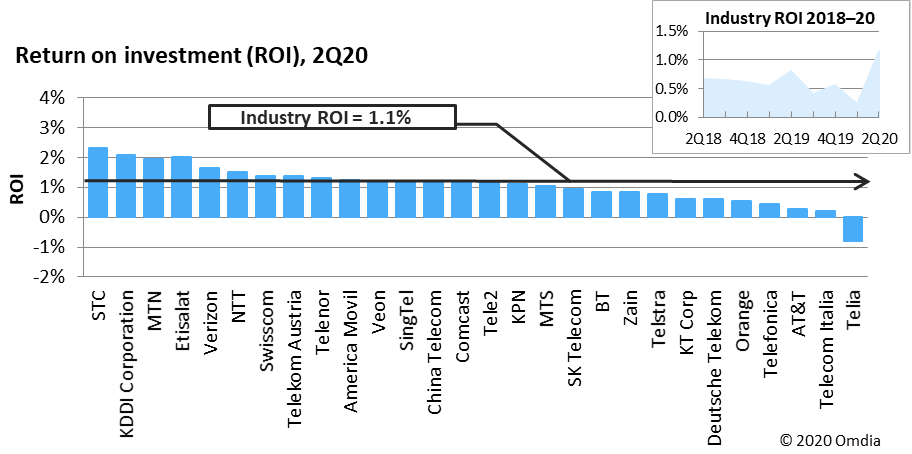
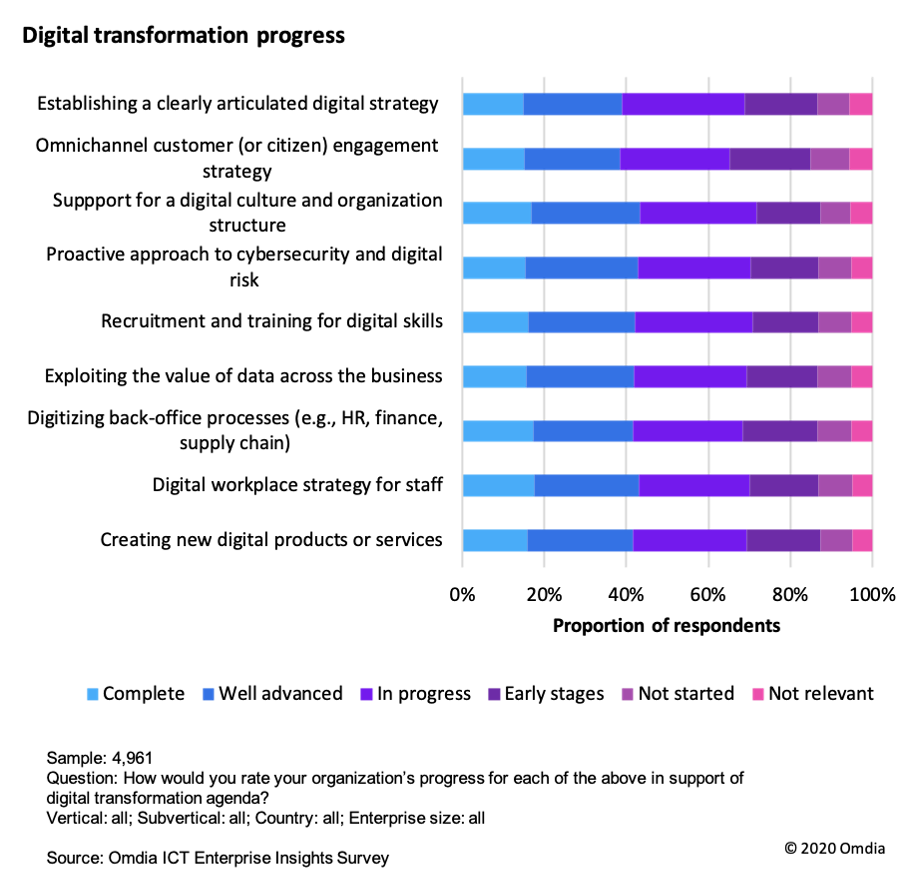
Macro trends in the ICT industry and technology evolution, and shifts in end-user and OTT demand, are also creating future opportunities for the broadband industry. The technological and commercial changes that these shifts drive also create new challenges, as broadband service providers and other stakeholders must try to keep ahead of changes while evolving sustainable business models.
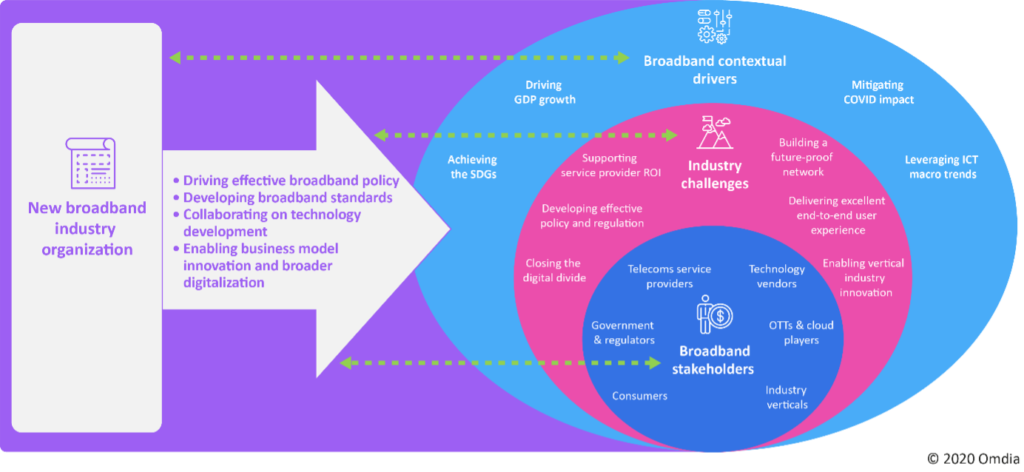
Broadband market stakeholders include operators, technology vendors, OTTs, governments and regulators, vertical industries, and consumers. Each has different requirements around broadband infrastructure and services. Policy and regulation around broadband and infrastructure play a key role in driving investment but are not always fully effective in creating a fair playing field that meets the needs of all stakeholders. This means widespread broadband access is still a goal rather than an achieved reality worldwide. It also means that the broadband industry itself is not developing as effectively as possible, which has knock-on impacts for both economic growth and social benefit.
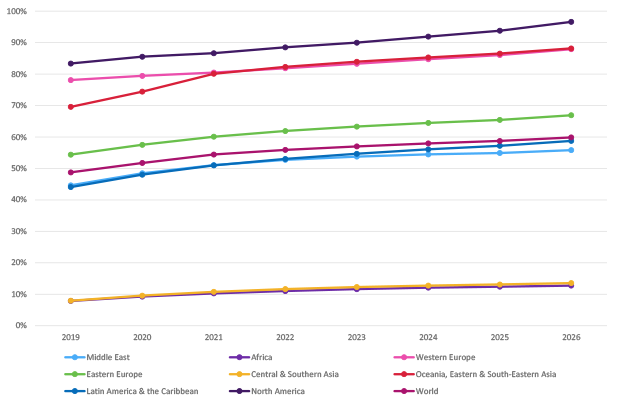
Inequality of broadband access is a continuing challenge for the industry overall and current efforts to address the digital divide effectively are not delivering impact quickly enough.
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted and accelerated the critical role of broadband in enabling consumers and enterprises to access work, education, and healthcare, as well as providing the means for enhanced communications as friends, families, and colleagues are separated for extended periods. This makes addressing the challenges facing the broadband industry even more urgent.
But to do so effectively is not simple or obvious for broadband industry stakeholders. Further complexity comes from the breadth and diversity of broadband stakeholders. These range from telecom service providers and technology vendors to a broad range of interested players, including vertical industries, regulators and governments, and internet/OTT providers.
To maximize the opportunity for positive development of the broadband industry, Omdia’s view is that the industry would benefit significantly from a new broadband industry organization to provide a neutral, collaborative platform for cooperation and partnership. This would enable more effective collaboration and co-creation among all industry stakeholders, to jointly address technical development, standards, commercial models, and other industry objectives and challenges. Such an organization could help ensure that broadband networks and services are available for all, and accelerate the healthy development of the industry, with sustainable benefits for stakeholders, end users, and society.